To ensure that financial statements are up to date, GAAP requires the use of accrual accounting. To practice accrual accounting, a business must follow the next two accounting principles:
Revenue Recognition Principle
The revenue recognition principle states that revenues should be recognized, or recorded, when they are earned, regardless of when cash is received.
Matching Principle
The matching principle states that expenses should be matched with the revenues they help to generate. In other words, expenses should be recorded when they are incurred, regardless of when they are paid.
Accruals
When revenues are earned before cash is received or expenses are incurred before cash is paid, it is called an accrual.
It is possible for a business to record revenues only when cash is received and record expenses only when cash is paid. This is referred to as cash accounting.
In many instances, when a company uses cash accounting, its financial statements do not present an accurate picture of how the company is performing. This is because a business may provide goods and services to customers “on account.” In this case, the business has earned revenue before it has received cash from the customer.
A business may also purchase goods and services from suppliers on account. In this case, expenses are incurred before cash is paid.
Deferrals
When cash is received for goods or services before the recognition of a revenue, or when cash is paid for goods or services before the recognition of the expense, it is called a deferral.
Businesses may also receive cash from customers before the delivery of goods or services to the customer. In this case, cash is received before revenue is earned.
In addition, businesses may pay for goods or services before receiving those goods or services from the supplier. In this case, cash is paid before an expense is incurred.
Accruals and deferrals can be summarized as follows:
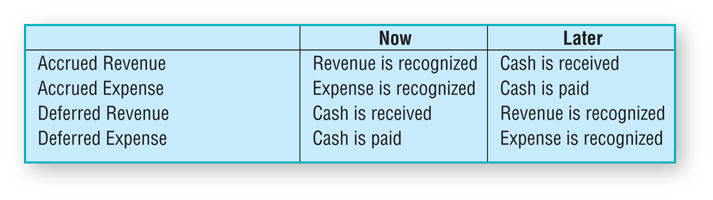
Figure: Accruals and deferrals Summary
Key Terms
Accrual accounting
Accounting method that records revenues when earned and expenses when incurred without regard to when cash is exchanged.
Revenue recognition principle
Recording revenues when they are earned by providing goods or services to customers.
Matching principle
Recording expenses in the time period they were incurred to produce revenues, thus matching them against the revenues earned during that same period.
Cash accounting
Accounting method that records revenues when cash is received and expenses when cash is paid.
Accruals
Revenues earned or expenses incurred before cash has been exchanged.
Deferrals
Cash received or paid before revenues have been earned or expenses have been incurred.