Equity is the third major element of the statement of financial position. The definition of equity is shown in the GAAP box.
| GAAP | Equity is ‘the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities’. |
Equity is the residual interest in the entity, calculated by subtracting liabilities from assets. The amount of equity, therefore, depends on the measurement of assets and liabilities. However, equity can be classified into different components. The most common categories are contributed capital, retained earnings and other reserves. Figure 1 graphically illustrates this division of equity.
FIGURE 1 Equity Elements
Example
Gulf Research LLC is based in Dubai. This international firm provides a broad range of services for the petroleum industry, including project management, drilling, reservoir testing, and well analysis. Some of these services require large investments in equipment.
Figure 2 shows the statement of financial position of Gulf Research LLC on 31 December 2009.
What Is Contributed Capital?
Contributed capital (also capital or paid-in capital) is the amount that the owners have invested in the business. As we know, investors are given shares as evidence of their ownership.
Contributed capital can be increased by selling additional shares to investors, and decreased when the business buys back its own shares from investors. Figure 2 shows that Gulf Research has capital totaling €275,000.
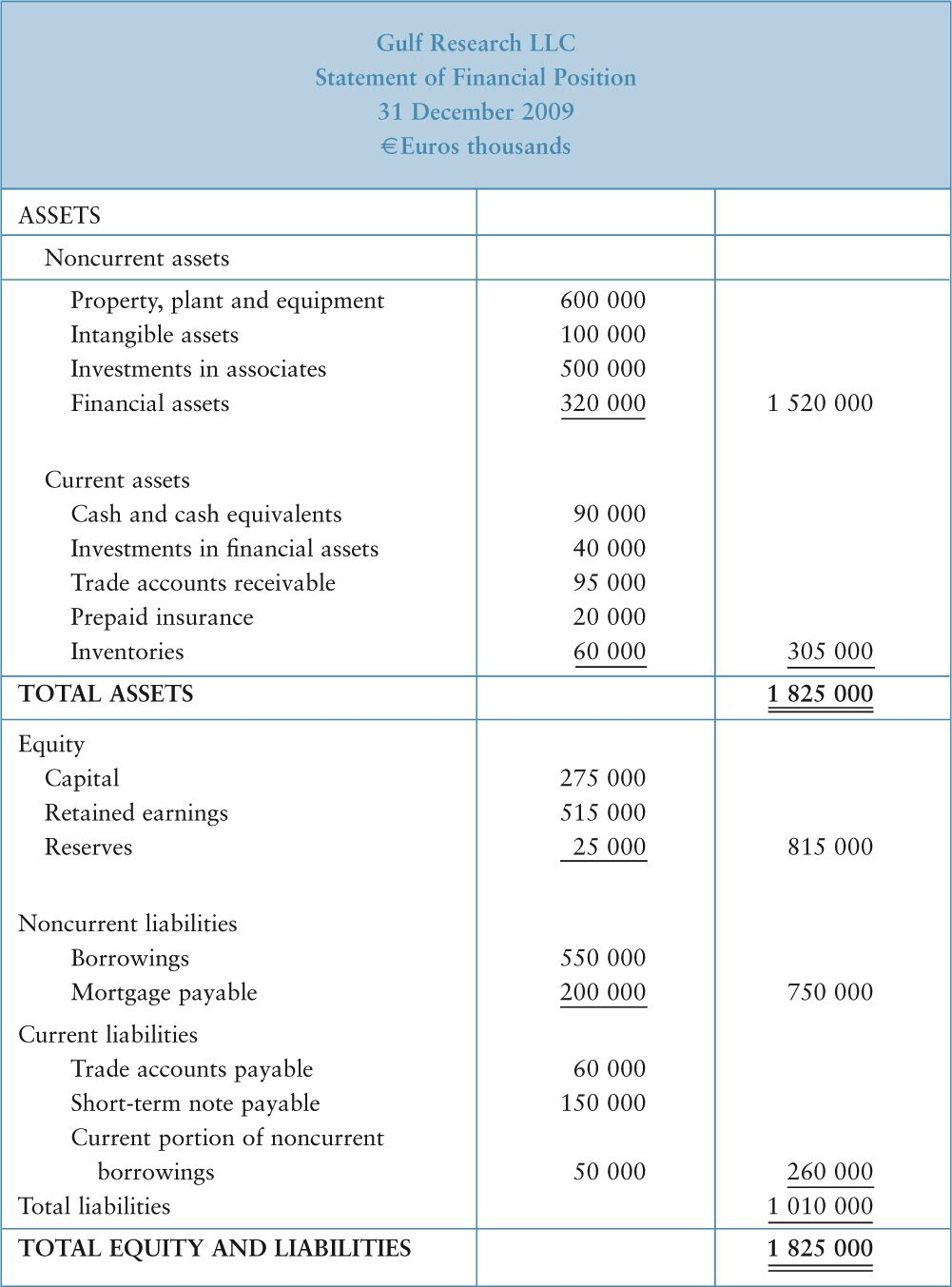
FIGURE 2 Statement of Financial Position
What Are Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings represent accumulated past earnings that have not been distributed to owners. Profit is added to and dividends are subtracted from equity. This is normally done through retained earnings. Of course, a loss would be subtracted from retained earnings.
What Are Reserves?
Reserves are created for different reasons. Management may create reserves for a variety of legal, statutory or other reasons.
A reserve can be created by appropriating a portion of retained earnings. For example, the board may set aside a portion of retained earnings as a reserve for an amount that the business expects to pay to managers and employees as bonuses.
Reserves can also be established through other comprehensive income. For example, a reserve could relate to the revaluation of an asset.
Figure 2 shows that Gulf Research has retained earnings of €515,000 and reserves of €25,000. Added to contributed capital these equal €815,000, which is the total equity balance. Equity and total liabilities tally to €1,825,000.
Key Terms of Equity
Equity
– The difference between assets and liabilities. Equity represents the business owners’ residual interest in the assets after all liabilities have been deducted.
Contributed capital
– The amount the owners have invested in the business.
Reserve
– Equity other than contributed capital that has been designated for a specific purpose.
Other comprehensive income
– Income that is not recognized in profit or loss.