In general, business entities can take one of three forms, as illustrated in Figure 1: a limited liability company, sole proprietorship or partnership.
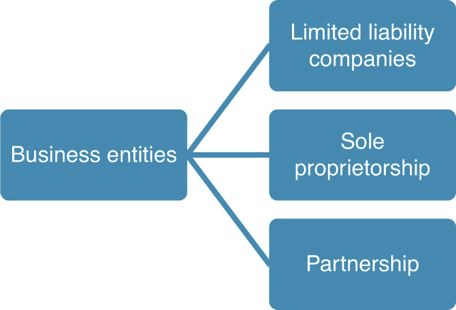
FIGURE 1 MAJOR FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A limited liability company is a legally independent entity established under the laws and regulations of the government in the jurisdiction where it is registered or incorporated.
Figure 2 lists examples of different forms that legal liability companies can take depending on the country or region. Although the legal rights granted to the entity and its owners vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, limited liability companies can typically own assets, create debt obligations, enter into legal contracts and engage in business transactions on their own.
When a limited liability company is created, we say that it has been registered or incorporated. Limited liability companies are sometimes referred to as corporations, joint stock companies or share-based entities.
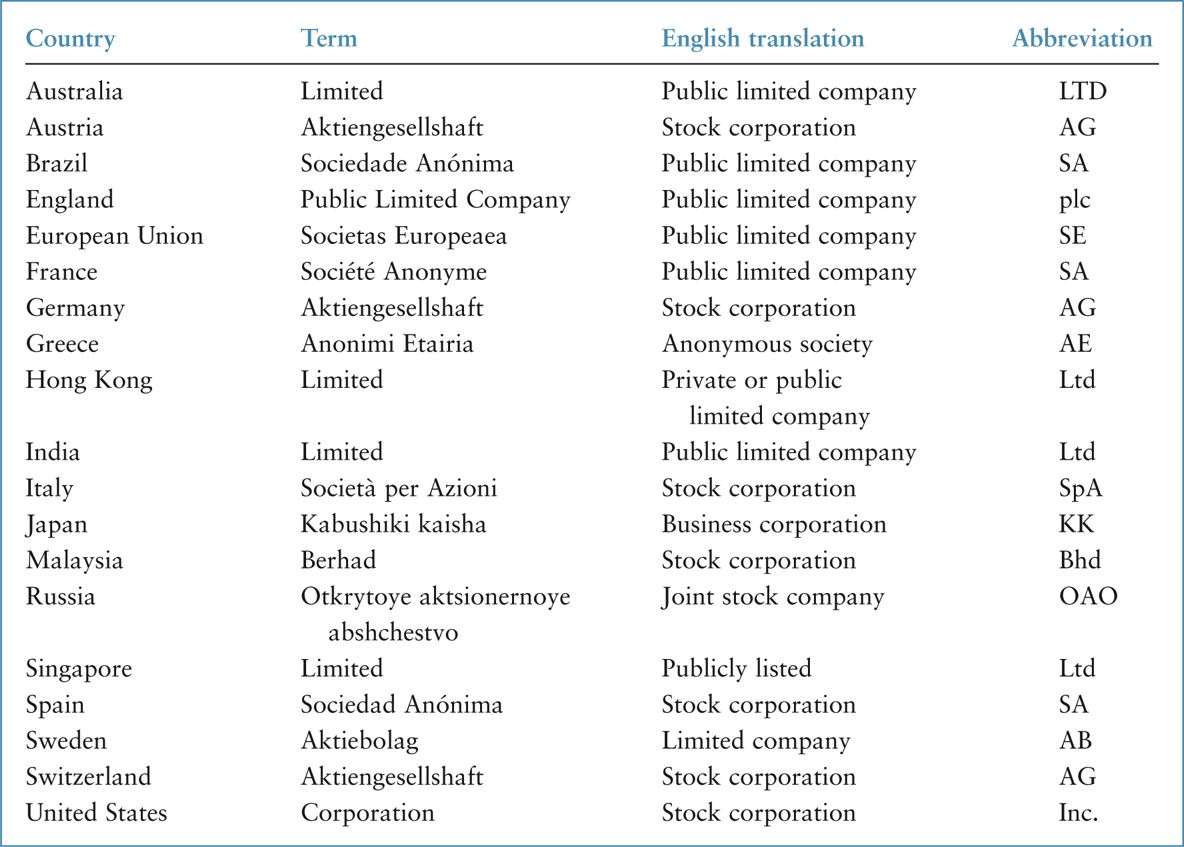
FIGURE 2 LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANIES IN DIFFERENT COUNTRIES
Advantages of LLC
Limited liability companies offer several advantages over the other two forms of business organization.
- They continue to operate even though changes in ownership occur. These changes are accomplished through the purchase and sale of shares, which provide evidence of ownership of the limited liability company.
- Moreover, since the limited liability company continues business operations uninterrupted, obtaining the financial resources it needs for growth is much easier.
- Shareholders also have limited liability, as the name implies. A shareholder can lose the amount that he or she has invested, but cannot ordinarily be pursued by creditors for payment of debts that are the obligations of the limited liability company.
Publicly Traded LLC
Some limited liability companies are publicly traded and all publicly traded companies are organized as limited liability companies. A publicly traded company is listed on an equity securities market (also known as a stock exchange or stock market ). Ownership of a large publicly traded company changes daily, as shares are frequently bought and sold on the world’s stock exchanges.
Figure 3 lists the world’s ten largest exchanges along with the total value of shares traded in billions of US dollars.
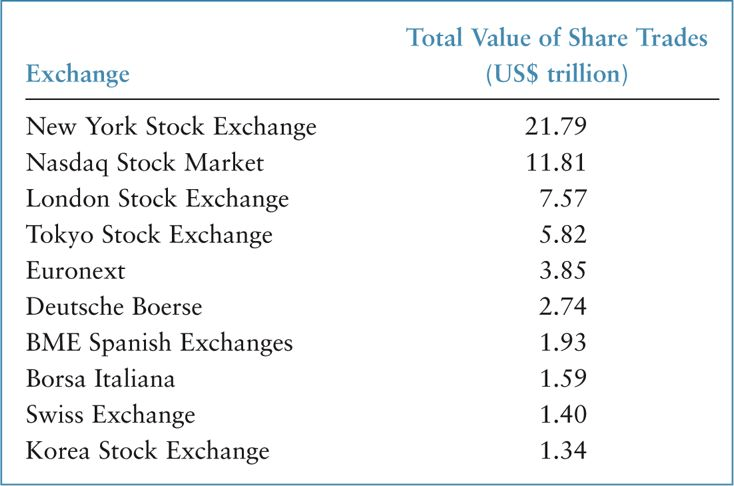
FIGURE 3 TEN LARGEST STOCK EXCHANGES
Privately Traded LLC
Limited liability companies that are not publicly traded are privately held (or closely held). Some privately held companies are quite large. For example, Koch Industries (www.kochind.com) is in chemicals and other diversified businesses, with an estimated $90 billion in annual sales and 85,000 employees.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can also be organized as limited liability companies, although most are privately held.
Sole Proprietorships
Privately held businesses can also take the legal form of a sole proprietorship or partnership.
A sole proprietorship is the simplest form of business organization and usually involves no legal registration. The owner (also known as a sole proprietor) conducts business under his or her own name.
In some cases, government authorities have provisions that allow a sole proprietor to adopt a fictitious name for trade purposes. For example, Didier Bihayintore, a sole proprietor, may conduct business under the name Didier’s Restaurant.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| The advantages of sole proprietorships are that they are simple and inexpensive to start since they require no registration, as already noted, and the cost of maintaining the business (for example accounting and legal fees) tends to be lower than for a limited liability company. | The disadvantages are that raising capital is more difficult. Usually, banks and other creditors lend capital to the sole proprietor rather than the business per se. This is because the business has no separate legal identity and therefore cannot engage in transactions or have legal obligations such as debt.
Another disadvantage is that the sole proprietor has no protection from creditors, who can pursue the owner for the collection of all business debts. |
Partnership
A partnership is an association of two or more persons or businesses as owners that conduct a business for profit. The owners are partners.
Partnerships are created by a partnership agreement (a private legal contract) among the partners that specifies how profits and losses will be shared, other compensation to be received by partners, and the responsibilities of partners.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| The advantage of partnerships is that more than one person can contribute resources and expertise to the business, and also share the responsibilities for managing the enterprise. | The disadvantages of partnerships are that individual partners are sometimes held accountable for obligations created by other partners for partnership purposes.
In addition, individual partners are not protected from creditors. A creditor may seek repayment of a partnership loan from all other partners or any one partner. When ownership changes – when one partner leaves or a new partner is admitted – the partnership must be legally dissolved and a new partnership created to replace it. |
Sole proprietorships and partnerships involve some differences in the owners’ legal rights and responsibilities, especially when compared to the limited liability company business organization. The exact form of these three types of business varies from one government jurisdiction to the next.
Hybrid forms of a business organization often exist that have features of two forms. For example, investors may be able to create a limited liability company that has some characteristics of a partnership.
While some variations also exist in how the ownership interests of sole proprietorships and partnerships are accounted for compared to limited liability companies, the accounting is generally the same.