The article highlights the essential skills, qualifications, and ethical standards required for an accountant, emphasizing the importance of analytical ability, communication, and professional certifications.
Two areas that impact financial reporting are (a) environmental, social, and governance reporting and (b) professional ethics.
ESG Reporting
Investors are becoming increasingly interested in a company’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategies. ESG reporting encompasses three elements:
- Environmental—issues related to climate change (e.g., carbon emissions), use of natural resources (e.g., water stress, biodiversity), pollution, and energy efficiency (e.g., renewable energy, green building).
- Social—issues focused on human capital (e.g., health and safety, labor management), social responsibility (e.g., diversity, equity, and inclusion), and product concerns (e.g., privacy and data security).
- Governance—issues related to company behavior and decision-making (e.g., business ethics, tax strategies, and transparency) and governance (e.g., board diversity, employee compensation).
A focus on ESG issues does not necessarily compromise a company’s financial performance. In fact, some evidence suggests that ESG strategies increase growth, reduce costs, ease regulatory pressure, improve productivity, and optimize capital allocation.
Although reporting on ESG issues is not currently required in the United States, many U.S. companies provide reports on ESG issues and this practice is expected to increase. For example, the European Union has recently approved the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive which significantly broadens the scope of sustainability reporting requirements. This Directive will not only effect EU-based companies but also U.S.-based companies with European operations.
Professional Ethics
For the economy to function effectively and efficiently, users must have faith that the information reported in financial statements is accurate and dependable. Accountants are often under intense pressure to apply the accounting standards to present a company in a favorable light. However, accountants serve the greater good of society and have an ethical responsibility to all the users who make decisions based on the financial information presented. Confidence that standards of ethical behavior will be maintained—even when individuals have incentives to violate those standards—is crucial to the financial reporting process.
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), recognizing that its members have an obligation of self-discipline above and beyond the requirements of generally accepted accounting principles, has adopted a code of professional conduct which provides ethical guidelines for accountants in the performance of their duties. These ethical principles require accountants to serve the public interest with integrity. For example, auditors should fulfill their duties with objectivity, independence, and due professional care. In no situation should an auditor yield to pressure from management to report positively on financial statements that overstate the company’s performance or prospects. Violation of these ethical standards can result in severe penalties, including revocation of an accountant’s license to practice as a certified public accountant.
Acting ethically is not always easy. The violation of ethical standards may not always bring clear and direct penalties; however, it often has subtle and long-lasting negative consequences for individuals and companies. Because of the important role of accounting in society, accountants are expected to maintain the highest level of ethical behavior.
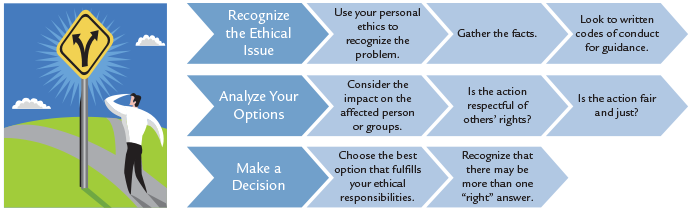
Figure 1. Guidelines in Ethical Decision-Making
Career Analysis
As you consider various career options, keep in mind that virtually every organization must have an accounting system. Thus, accountants are employed in a wide range of businesses, including private companies, public accounting firms, governments, and banks. To help you evaluate whether an accounting career is right for you, consider the following question:
What skills and character traits are required for accountants?
Accountants must have well-developed analytical skills and must be effective communicators, both verbally and in writing. Most accounting assignments—whether in business, government, or public accounting—are team assignments in which team members must be able to communicate effectively and work quickly and cooperatively to a solution.
As a profession, accounting requires a high level of academic study and is subject to professional competence requirements. Most members of public accounting firms, and many management accountants and consultants, are (or are in the process of becoming) Certified Public Accountants (CPAs). Other valuable professional certifications are the Certified Management Accountant (CMA), the Certified Internal Auditor (CIA), and the Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE) designations. All of these designations are designed to ensure that the accountants who offer their services are properly qualified and maintain a high level of personal integrity and ethical behavior.
While the career opportunities for accountants are virtually boundless, even if you choose a different career path, the knowledge and experience that you can gain from accounting will prove invaluable in your career.
Accountants must possess strong analytical and communication skills, demonstrate professional competency, and behave ethically.
Key Takeaways
The combination of analytical skills, effective communication, professional competence, and ethical behavior is essential for success in accounting and related fields. These qualities enable accountants to interpret complex financial data, collaborate efficiently within teams, and make informed business decisions. Furthermore, professional certifications such as CPA, CMA, CIA, and CFE not only validate an accountant’s expertise but also enhance credibility and career advancement opportunities. Ultimately, these skills and qualifications ensure accuracy, transparency, and trust—key elements that support sound financial management and sustainable organizational growth.