An expected value in the future is ‘discounted’ to reflect today’s value, assuming a positive return on investment or inflation rate.
Essentially one dollar in the future is not worth as much as one dollar today; the future dollar is worth less than today’s dollar, hence discounted.
Formula
The FV formula is essentially an inverse of the PV formula and is reflected by the following:
\[FV=PV{{\left( 1+i \right)}^{n}}\]
•Present value (PV) is the value of an investment today, at time zero;
•Future value (FV) is the value of today’s investment at a future point of time;
•‘n’ is the amount of periods, often in years, in the future; and
•‘i’ is the assumed interest rate an investment is projected to earn.
An abbreviated FV table is included here as Table 1.
Example
A simple 1 million dollars investment made today at 5% interest in 20 years would have a value of 2,650,000 dollars as represented in the following formula. This also can be calculated simply from our table by multiplying 1,000,000 dollars by 265/100.
\[FV=\$1,000,000{{\left(1+0.05\right)}^{20}}=\$2,650,000\]
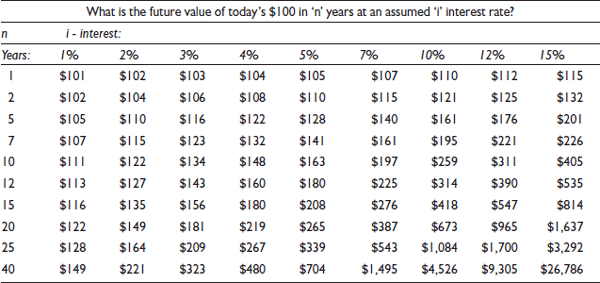
Table 1 Future value Table