The article explains the importance of accounting in business and everyday life, describing how it provides financial information for decision-making, supports internal and external users, and enhances transparency through financial reporting and data analysis. It also highlights how accounting uses data analytics to improve efficiency, manage risks, and guide future actions.
Our economy is comprised of many different businesses. Some companies focus on providing goods, which for Apple take many forms, including desktop and laptop computers, iPads, iPhones, and wearables such as Apple Watches. Other companies are primarily concerned with providing services. For example, The Walt Disney Company offers a variety of entertainment services from theme parks to motion pictures to streaming videos. While most entities, like Apple and Disney, exist in order to earn a profit, some are organized to achieve other benefits to society (e.g., school districts exist to meet the educational needs of a community). Regardless of their objective, all entities use accounting to plan future operations, make decisions, and evaluate performance.
Accounting is an information system that identifies, measures, records, and communicates financial information about a company’s business activities so decision-makers can make informed decisions. Without adequate information users will not be able to judge a business’s economic opportunities and risks. Accounting is the “language of business” because it communicates information about the economic activities of a company that helps people make better decisions.
Users of Accounting Information
The demand for accounting information comes from both inside and outside the business and is summarized in Figure 1. Inside the business, managers use accounting information to help them plan and make decisions about the company. For example, managers use accounting information to help decide which actions to take, predict the consequences of their actions, and control the operations of the company. Accounting that is designed to meet the needs of internal users is called managerial accounting.
Outside the business, investors (owners) use accounting information to evaluate the future prospects of a company and decide where to invest their money. Creditors (lenders) use accounting information to evaluate whether to loan money to a company. Other external users include governmental agencies that use accounting information to determine taxes owed by companies, to implement regulatory objectives, and to make policy decisions; labor unions that are negotiating wage increases for its members; and financial analysts offering buy or sell recommendations to clients.
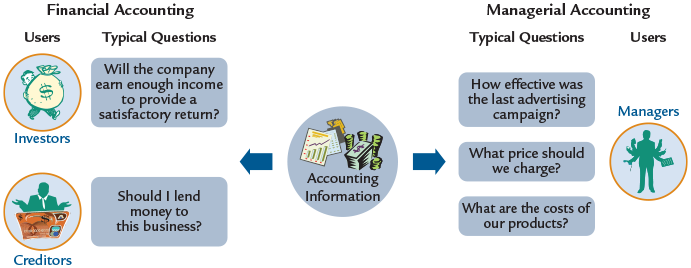
Figure 1. The Demand for Accounting Information
How will accounting affect my life?
Accounting will impact many aspects of your daily life. The business that sells you goods or services uses accounting to keep track of how much money it received as well as the cost of operating the business. Calculating the amount of tax that is owed to the government requires accounting. When you invest your money, you should use accounting to understand a company’s business and its prospects for the future. Plans that you make for the future often involve accounting to determine how much money you will need.
Financial Reporting and Data Analysis
Financial reporting (more broadly referred to as disclosure) is the process of communicating financial accounting information to external decision-makers. In addition to allowing investors to make informed decisions, the full disclosure of all relevant accounting information increases the transparency of a company’s operations, reduces the risk of manipulation and fraud, and adds stability to the capital markets.
The objective of financial accounting and reporting involves providing external decision-makers with information that assists them in assessing the amounts, timing, and uncertainties of a company’s future cash flows. This information is provided through four basic financial statements: the balance sheet, the income statement, the retained earnings statement, and the statement of cash flows. In addition, the financial statements should include notes that clarify and expand on the information presented in the financial statements.
Data analytics is the process of analyzing data so that businesses can make decisions more efficiently. Because accounting’s role is to provide useful information to internal and external users, it is well-positioned to use data analytics to help companies gain valuable insights. These insights can help to improve financial reports, identify opportunities for increased operational efficiency, and better manage risks. For example, the executive VP and CEO of the Boston Red Sox uses data analytics to increase profits and optimize the sports fan experience.
Data analytics can be descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, or prescriptive. The chart below provides a description and example of each type:
| Type | Description | Example |
| Descriptive | Describes what has happened or summarizes outcomes | Did we meet our sales quota for the month? |
| Diagnostic | Explains why things happened by trying to understand how variables are related | Is there a relation between the volume of product sold and its appearance in a video with a popular YouTuber? |
| Predictive | Attempts to predict what will happen in the future | What is the probability of the video going viral, and is this likely to lead to increased product demand? |
| Prescriptive | Recommends a possible course of action | If the video has a 70% probability of going viral, we should increase production. |
Key Takeaways
Accounting and its related practices—such as financial reporting and data analysis—are essential for effective business management and decision-making. They provide accurate financial information that supports planning, evaluation, and transparency, helping both internal and external users make informed choices. The application of accounting in areas like budgeting, investment decisions, and risk management ensures organizational efficiency and stability, while the integration of data analytics further enhances accuracy, foresight, and overall business success.