Activity-based budgeting is budgeting based on activities rather than units, products, or departments. An extension of ABB.
Activity-based budgeting is based around activities; it centers on the information generated through the activity-based costing (ABC) system, focusing on the operations of the business within the value chain.
Activity-based budgeting is gaining significant use in very large organizations. The process of creating Activity-based budgeting (ABB) is as follows:
- Analyze products and customers to be able to predict the production and sales demand.
- Use the information from the ABC system to estimate the resources required to perform organizational activities.
- With demand predicted, estimate the quantity of each resource that will be needed to meet the demand.
- Allocate resources based on these predictions for each activity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
See the advantages and disadvantages of activity-based budgeting in Figure 1.
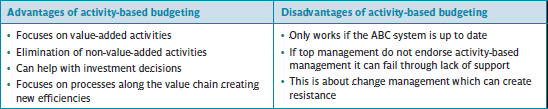
Figure 1: Advantages and disadvantages of activity-based budgeting